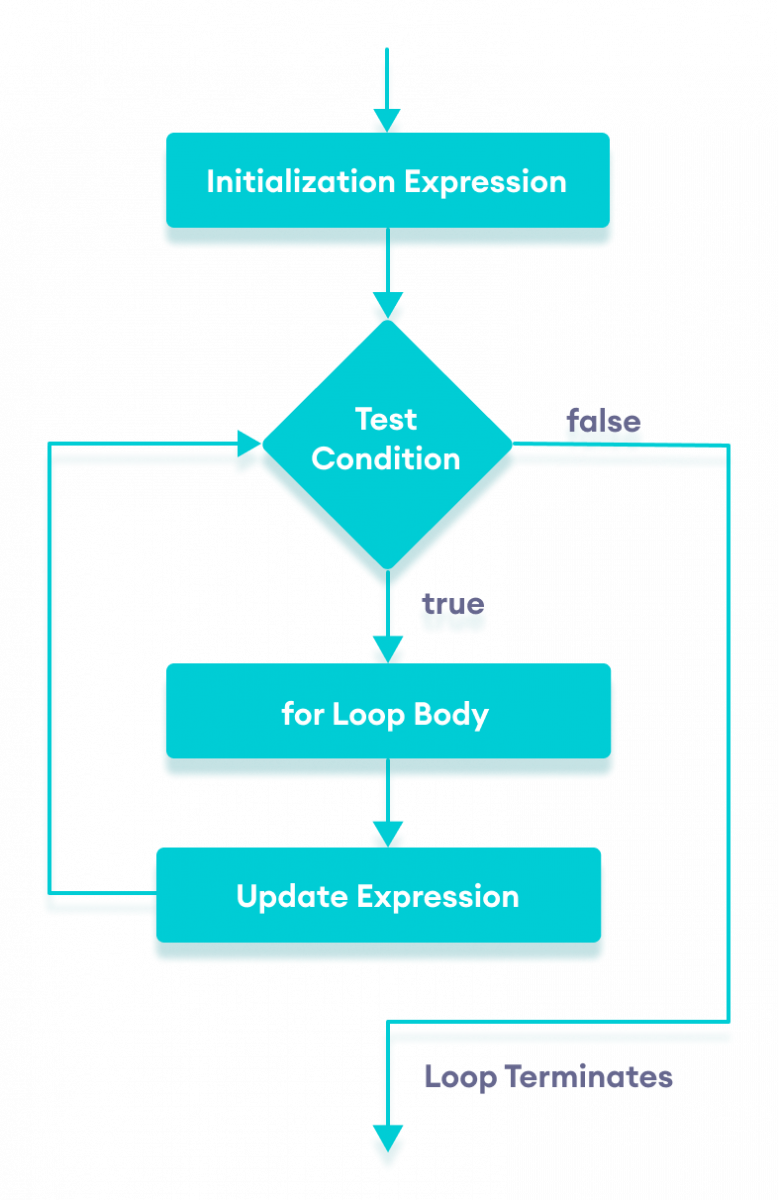
 loop in Java with flowchart" width="320" height="493" />
loop in Java with flowchart" width="320" height="493" />In computer programming, loops are used to repeat a block of code. For example, if you want to show a message 100 times, then rather than typing the same code 100 times, you can use a loop.
In Java, there are three types of loops.
This tutorial focuses on the for loop. You will learn about the other types of loops in the upcoming tutorials.
Java for loop is used to run a block of code for a certain number of times. The syntax of for loop is:
for (initialExpression; testExpression; updateExpression) < // body of the loop >To learn more about the conditions, visit Java relational and logical operators.
 loop in Java with flowchart" width="320" height="493" />
loop in Java with flowchart" width="320" height="493" />
// Program to print a text 5 times class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int n = 5; // for loop for (int i = 1; i > >Output
Java is fun Java is fun Java is fun Java is fun Java is fun
Here is how this program works.
| Iteration | Variable | Condition: i | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1 n = 5 | true | Java is fun is printed. i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2 n = 5 | true | Java is fun is printed. i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3 n = 5 | true | Java is fun is printed. i is increased to 4. |
| 4th | i = 4 n = 5 | true | Java is fun is printed. i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5 n = 5 | true | Java is fun is printed. i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6 n = 5 | false | The loop is terminated. |
// Program to print numbers from 1 to 5 class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int n = 5; // for loop for (int i = 1; i > >Output
1 2 3 4 5
Here is how the program works.
| Iteration | Variable | Condition: i | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | i = 1 n = 5 | true | 1 is printed. i is increased to 2. |
| 2nd | i = 2 n = 5 | true | 2 is printed. i is increased to 3. |
| 3rd | i = 3 n = 5 | true | 3 is printed. i is increased to 4. |
| 4th | i = 4 n = 5 | true | 4 is printed. i is increased to 5. |
| 5th | i = 5 n = 5 | true | 5 is printed. i is increased to 6. |
| 6th | i = 6 n = 5 | false | The loop is terminated. |
// Program to find the sum of natural numbers from 1 to 1000. class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int sum = 0; int n = 1000; // for loop for (int i = 1; i System.out.println("Sum java-exec"> // Program to find the sum of natural numbers from 1 to 1000. class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < int sum = 0; int n = 1000; // for loop for (int i = n; i >= 1; --i) < // body inside for loop sum += i; // sum = sum + i >System.out.println("Sum /java-programming/arrays">arrays and collections. For example, // print array elements class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < // create an array int[] numbers = ; // iterating through the array for (int number: numbers) < System.out.println(number); >> >
Output
3 7 5 -5
Here, we have used the for-each loop to print each element of the numbers array one by one.
In the first iteration of the loop, number will be 3, number will be 7 in second iteration and so on.
Java Infinite for Loop
If we set the test expression in such a way that it never evaluates to false , the for loop will run forever. This is called infinite for loop. For example,
// Infinite for Loop class Infinite < public static void main(String[] args) < int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i > >
Also Read:
- Enhanced For Loop
- Nested Loop
- Break Statement
- Continue Statement
